Surgical treatment of thyroid
gland diseases
The thyroid gland is an endocrine organ located in the lower part of the front of the neck, just above the breastbone. Its task is to produce the hormones Triiodothyronine and Thyroxine - labeled as T3 and T4 in laboratory analyses, which regulate numerous metabolic processes in the body. The number of hormones produced by the thyroid gland during the day is regulated by another endocrine gland - the pituitary gland, through its thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
Diseases of the thyroid gland are manifested in two ways:
1) by dysfunction, when the gland produces more (hyperthyroidism) or less hormone (hypothyroidism) than the body needs;
2) by a structural disorder, when tumors (nodules) and cysts form in the gland, or the gland enlarges diffusely. Thyroid disease is usually caused by autoimmune disorders, diagnosed by laboratory analysis - a high titer of autoantibodies to some of the structural elements of the gland (anti-TPO, anti-Tg...) - the so-called Hashimoto's thyroiditis.

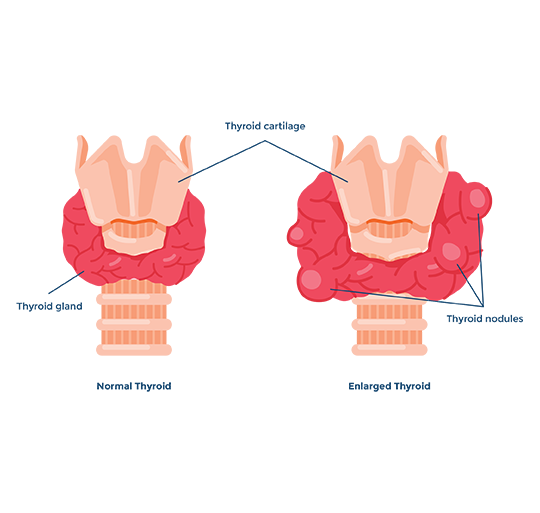
How can you become aware of a thyroid gland disease?
Hyperthyroidism manifests in weight loss, increased sweating, rapid pulse, tremors, nervousness... Hypothyroidism leads to obesity, sluggishness, sleepiness, depression...
Structural changes in the thyroid gland tissue may not cause any subjective difficulties or may create a feeling of pressure. In many cases, the nodule can be noticed from the outside, like a lump under the skin in the thyroid gland area, and also be palpable without the patient feeling anything. The feeling of pressure and a lump in the throat is a common neurotic symptom perceived as a thyroid gland disease. Examining the thyroid gland in such cases is helpful for the patient to be psychologically relieved.
What thyroid gland diseases are the reason for surgery?
1) Functional disorders are primarily treated with drugs. Hyperthyroidism surgery is approached only when drug therapy becomes insufficient or lasts too long. Hypothyroidism never requires surgical treatment unless there is a tumor in the thyroid gland that needs to be surgically removed.
2) Tumors (nodules) of the thyroid gland are mostly harmless (benign) changes, which, as long as less than 2 cm in diameter, do not require surgery but only need to be monitored by periodic ultrasound examinations. However, nodules require surgery in the following cases:
- when there is a suspicion that the nodule in the gland is actually cancer; an experienced surgeon will assess this based on clinical and ultrasound examination; thyroid fine needle aspiration biopsies (FNA) are not required for this purpose; surgeons of M.C. Aesculap do them exceptionally rarely.
- when the nodule in the thyroid gland, due to its size, creates compressive disorders (difficulty swallowing, feeling of pressure...), or creates a lump on the neck that is aesthetically unappealing.
- when the nodule increases over time, which is registered by periodic ultrasound examinations; surgery is usually suggested when it grows beyond 2cm in size.

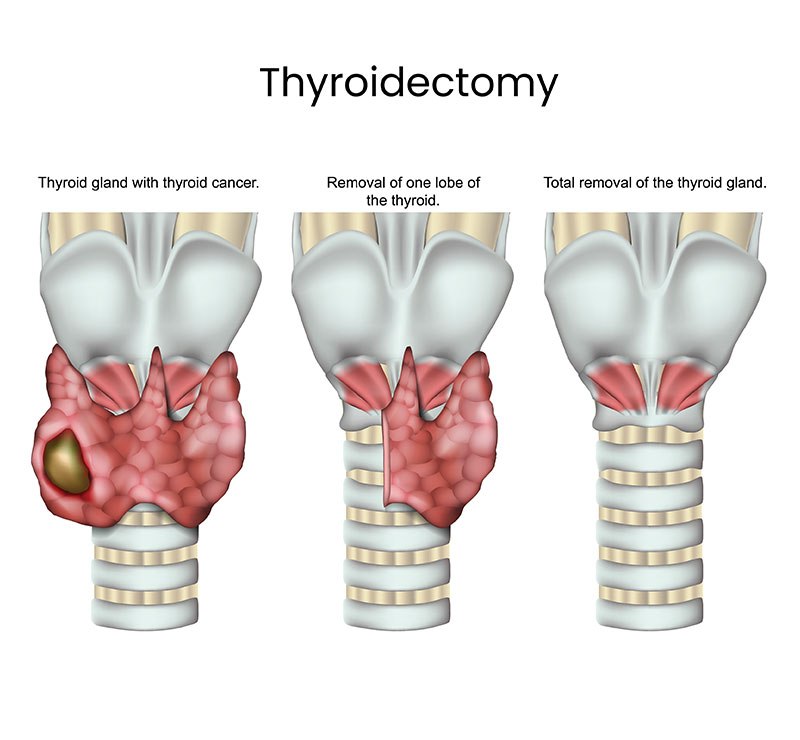
Thyroid surgery
Indications for surgery are functional and morphological disorders of the thyroid gland. Especially in the case of functional diseases (hyperthyroidism), we are guided by the principle that the proposal for surgery should come from the endocrinologist, who also carries out preoperative thyrosuppressive therapy and postoperative monitoring of gland function.
Node surgery involves lobectomy on the affected side, with ex tempore analysis. If it is a malignant tumor, total thyroidectomy and exploration of the central and lower jugulocarotid lymphatics on the tumor side are performed; if the glands are negative, the surgery ends there; if they are positive, a functional neck dissection is performed on the affected side.
Be responsible, and get checked on time.
Aesculap team of surgical oncologists
Prof. dr sci. med. Nebojša Ivanović
Specijalista onkološke hirurgije
Doktor nauka u oblasti onkološke hirurgije. Profesor na Katedri za hirurgiju Medicinskog fakulteta u Beogradu. Osnivač bolice Aesculap.
Ass dr Nataša Čolaković
Specijalista opšte hirurgije
Opšti hirurg dr Nataša Čolaković je lekar bolnice Bežanijska kosa kao i članica stručnog hirurškog tima bolice Aesculap
dr Simona Petričević
Specijalista opšte hirurgije
Dr Simona Petričević je specijalista opšte hirurgije na doktorskim studijama iz onkoloske hirurgije.